Out of state clients use this requisition when sending PNH testing
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) Requisition for Out of State Clients
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Clinical Significance:
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare but life threatening and debilitating disease. Clinically, PNH is characterized by chronic intravascular hemolysis, bone marrow failure and life threatening thrombosis. PNH evolves from a hematopoietic stem cell defect in which a somatic mutation of an x-linked gene (PIG-A) results in a partial or absolute deficiency of GPI-linked proteins. Absent or markedly diminished expression of GPI-linked antigens is specific for all patients with PNH.
Who should be tested:
Patients with aplastic anemia (AA), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), bone marrow failure syndromes or unexplained hemolysis.
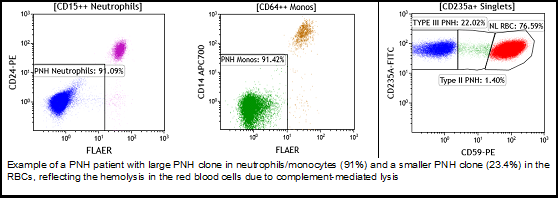
Antibody Panels:
RBC panel: CD235a-CD59
WBC panel: FLAER-CD24-CD15-CD64-CD14-CD45 (monocytes and granulocytes)
Specimens:
1-2 ml peripheral blood in EDTA or heparin (4 °C or room temperature).
Forms:
Dahl-Chase Flow Cytometry requisition form, demographic sheet and recent CBC results.
Transport:
Specimens need to be delivered and analyzed within 24-48 hours.
Flow Cytometry lab should be notified of coming specimen with shipment alert
UniShip courier pick-up available for in-state specimens
FedEx pick-up available for out-of-state specimens
CPT codes:
88184, 88185 x 7, 88187
Test performed:
Monday through Saturday.
Tet reported:
Faxed or mailed within 24 hours after sample is received.
References:
1. Borowitz et al: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of PNH and Related Disorders, Clin Cytometry 2010, 211-230
2. Sutherland et al: Practical guidelines for the high-sensitivity detection and monitoring of PNH clones by flow cytometry. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2012; 82:195-208.
3. ICCS/ESCCA PNH consensus Guidelines 2018, 4 part series in Cytometry B
