DNA Ploidy and Cell Cycle Analysis
Clinical Significance
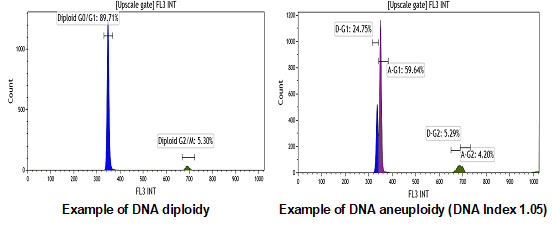
Nuclear DNA content can be measured and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the DNA ploidy of the sample. Normal cells have a diploid DNA content while many tumors show cells with an abnormal DNA content (aneuploidy). Cell cycle analysis may be used to determine the proliferative activity of a neoplasm. The presence of aneuploidy is typically associated with a neoplastic process. It usually is considered a bad prognostic factor in many solid tumors but has positive implication regarding treatment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia, neuroblastoma and medulloblastoma. DNA ploidy is usually not used as a stand-alone test but rather as an additional marker together with immunophenotyping to test for an abnormal population.
Specimens
Bone marrow in Na Heparin
Peripheral blood in EDTA
Lymph node or other biopsy in Flow Cytometry medium
Body fluids in RPMI medium or saline
Forms
Dahl-Chase Flow Cytometry requisition form along with demographic sheet
Transport
Fresh Specimens need to be delivered and analyzed within 24-48 hours via Uniship Courier.
CPT code
88182
Test performed
Monday through Saturday.
Test reported
Faxed or mailed within 24 hours after sample is received.
